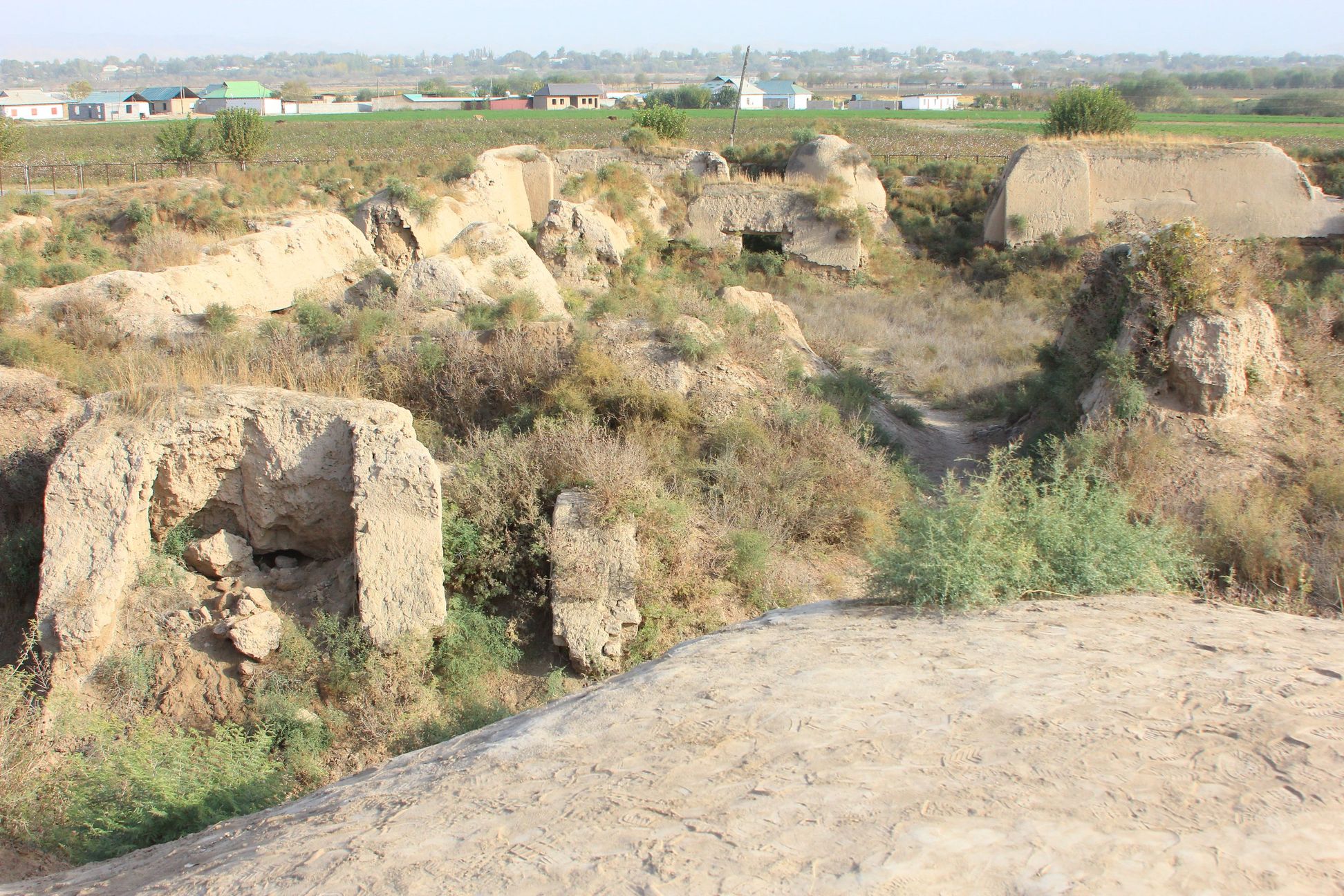
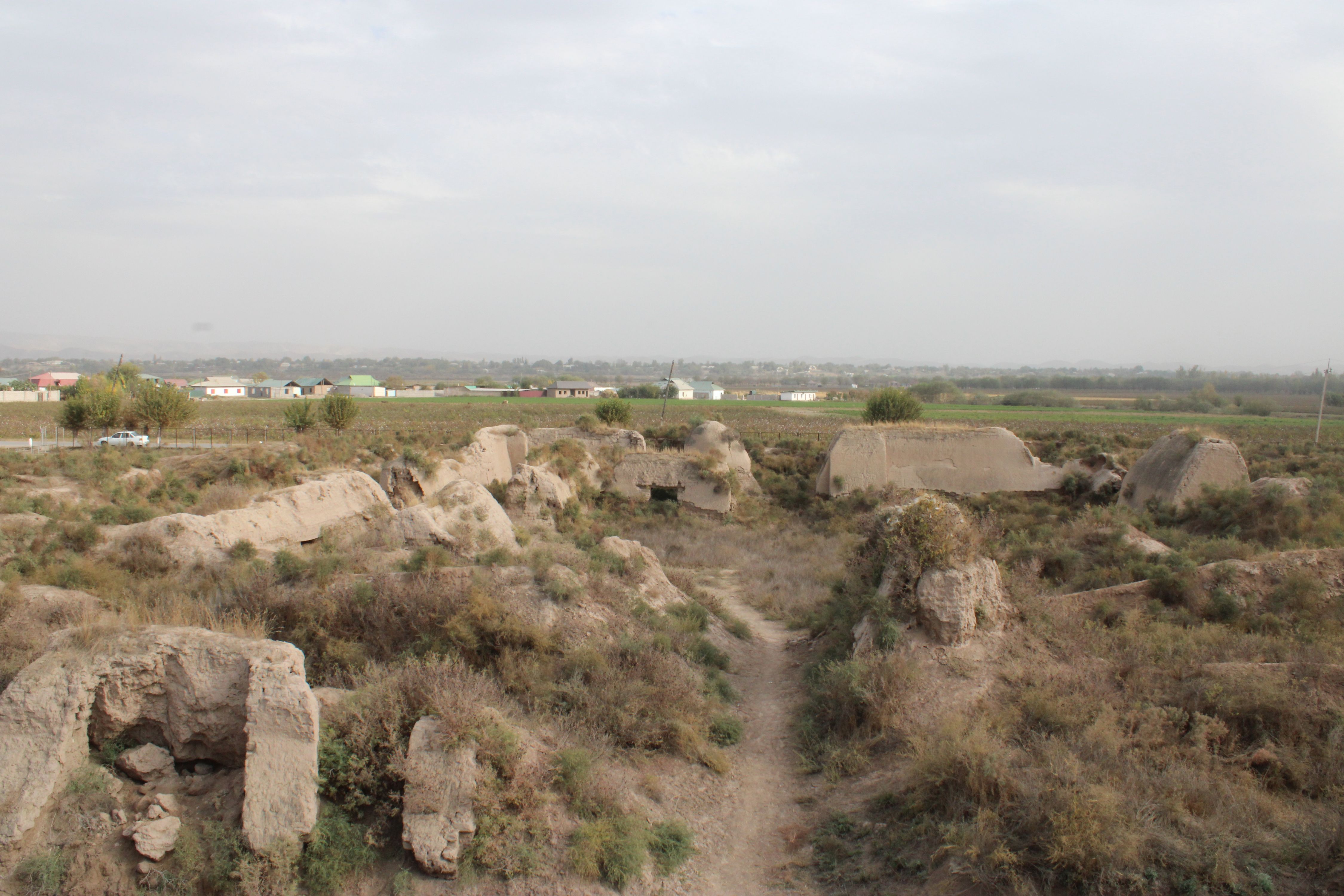
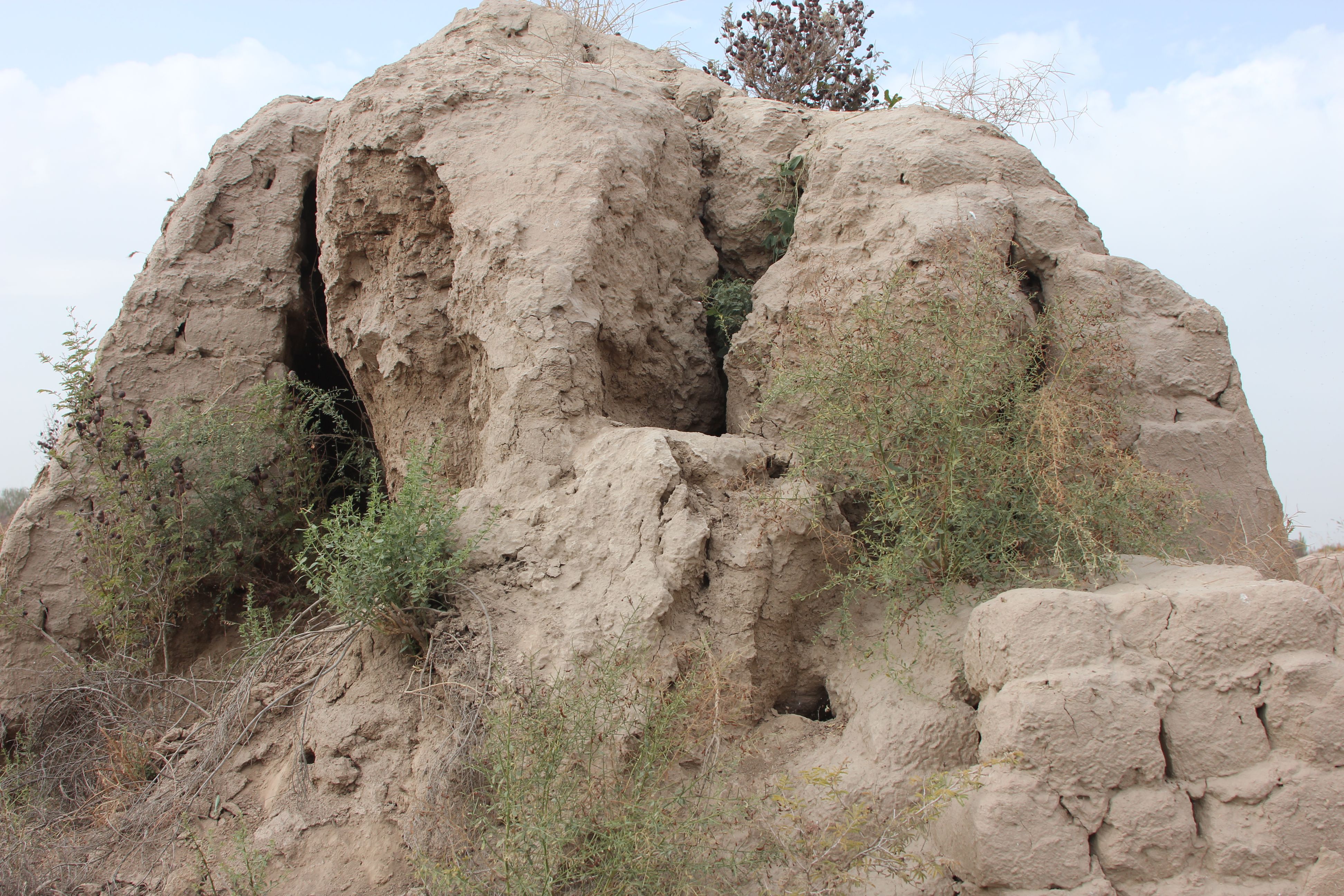
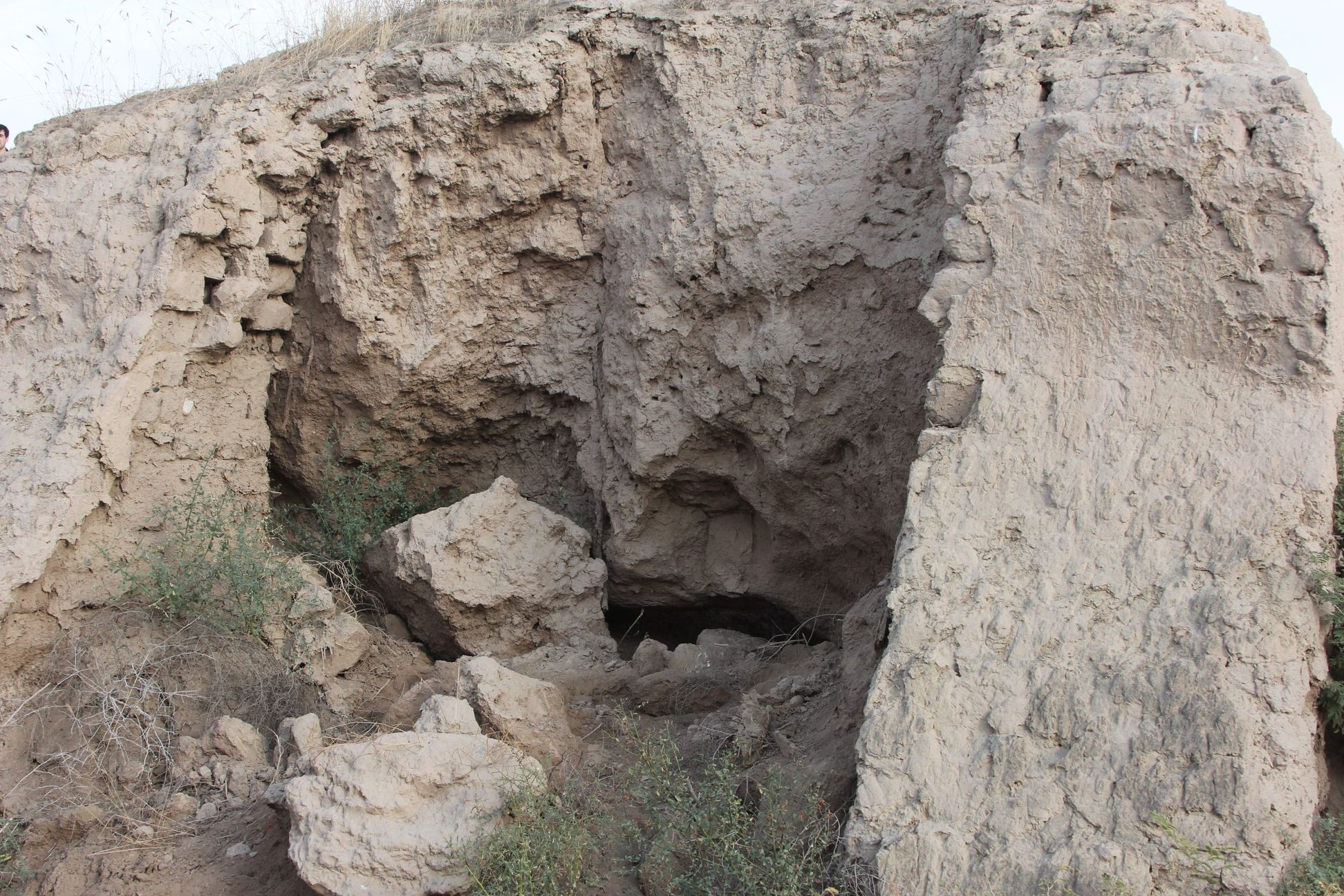
The ruin of the Buddhist cloister of of Ajina-Tepa (Devil’s Hill) is located in the southwestern part of Kizilsoy village in the Wakhsh district of Khatlon province. This ancient monument is situated 12 km north of the Bokhtar city (former Qurghonteppa). The site is approximately 85 km far to the south of the capital city Dushanbe and around 53 km away from Tajikistan’s border with Afghanistan in the opposite direction. An approximate elevation of the site is 430 meters above sea level. In a wider geographical context, Ajina-Tepa is located in a valley within the lower stream of Wakhsh river surrounded by mountains almost on all sides.

Architectural Features
The Ajina-Tepa complex functioned around the seventh and eighth centuries AD. It was a typical Buddhist building with the size 50 x 100 m, combining two monasteries: the Vihara monastery and the Sangharama, the place where the Buddhist monastic community lived. It had two parts: the southeastern monastery and the temple halves. It was a renowned religious centre for the Buddhist monks. The Buddhist monastery of Ajina-Tepa had a special room, where a painted clay colossus lied on a pedestal.
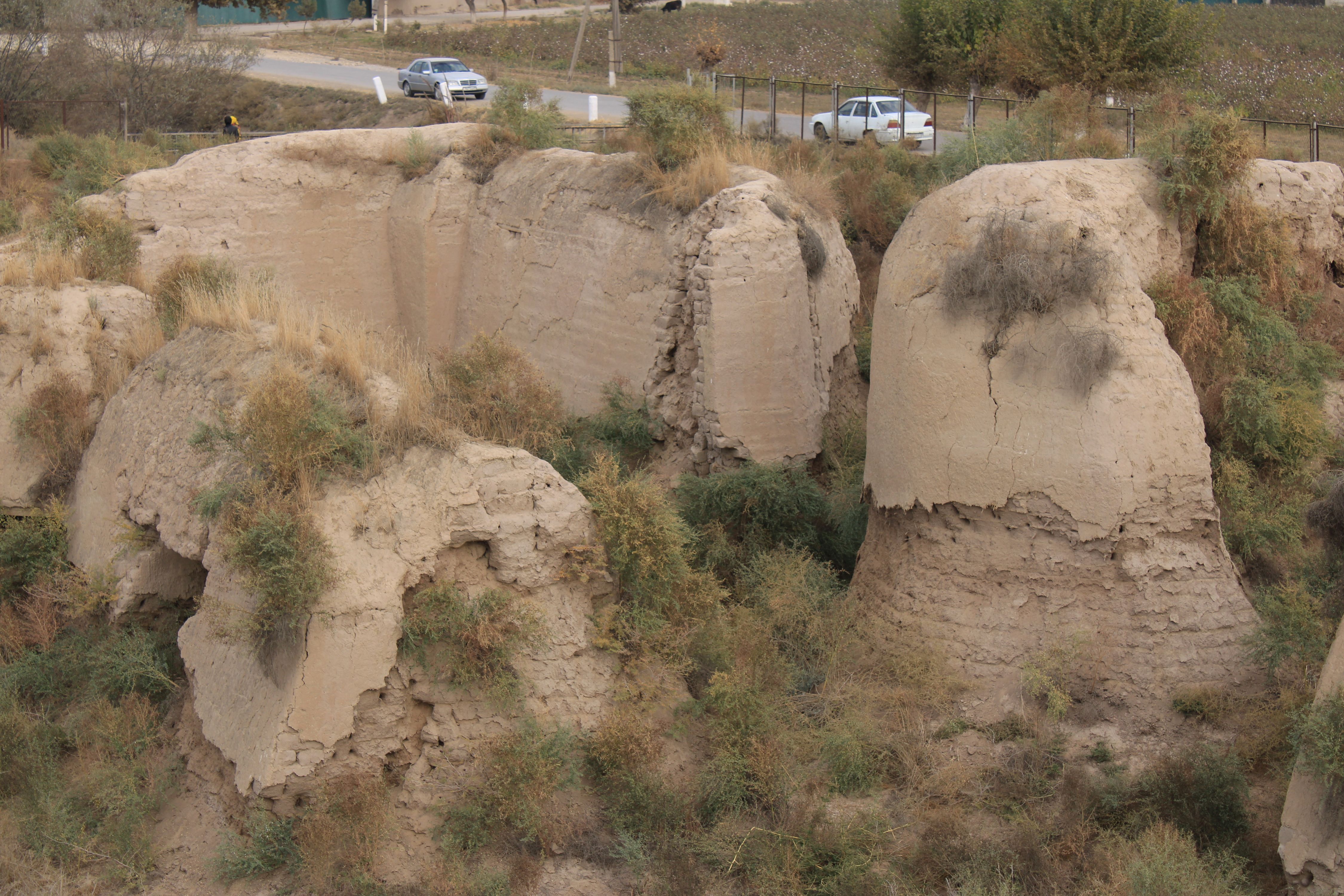

History
Ajina-Tepa monument is a synthesis of the traditions and images of Indian art and the local Bactrian- Tocharistan heritage. These masterpieces of art show how Buddhist artistic creativity reached its peak in Central Asia in the 7th-8th centuries. Some archeologists are of view that the monastery was destroyed in during the spread of Islam into the area from c. 750 AD onwards. Recent archaeological interpretations refer to the fact that the abandoned sites may have gradually decayed, rather being deliberately destroyed.
Sleeping Buddha
During many of excavation large numbers of diverse and spectacular artefacts were discovered in the site.
The final collection of artefacts from the site included over 600 art works, over hundred sculptures, fragments of large sculpture groups, and a large numismatic collection (about 300 copies of copper coins). Most of the artefacts were taken to the state Hermitage Museum, St Petersburg after the excavation.
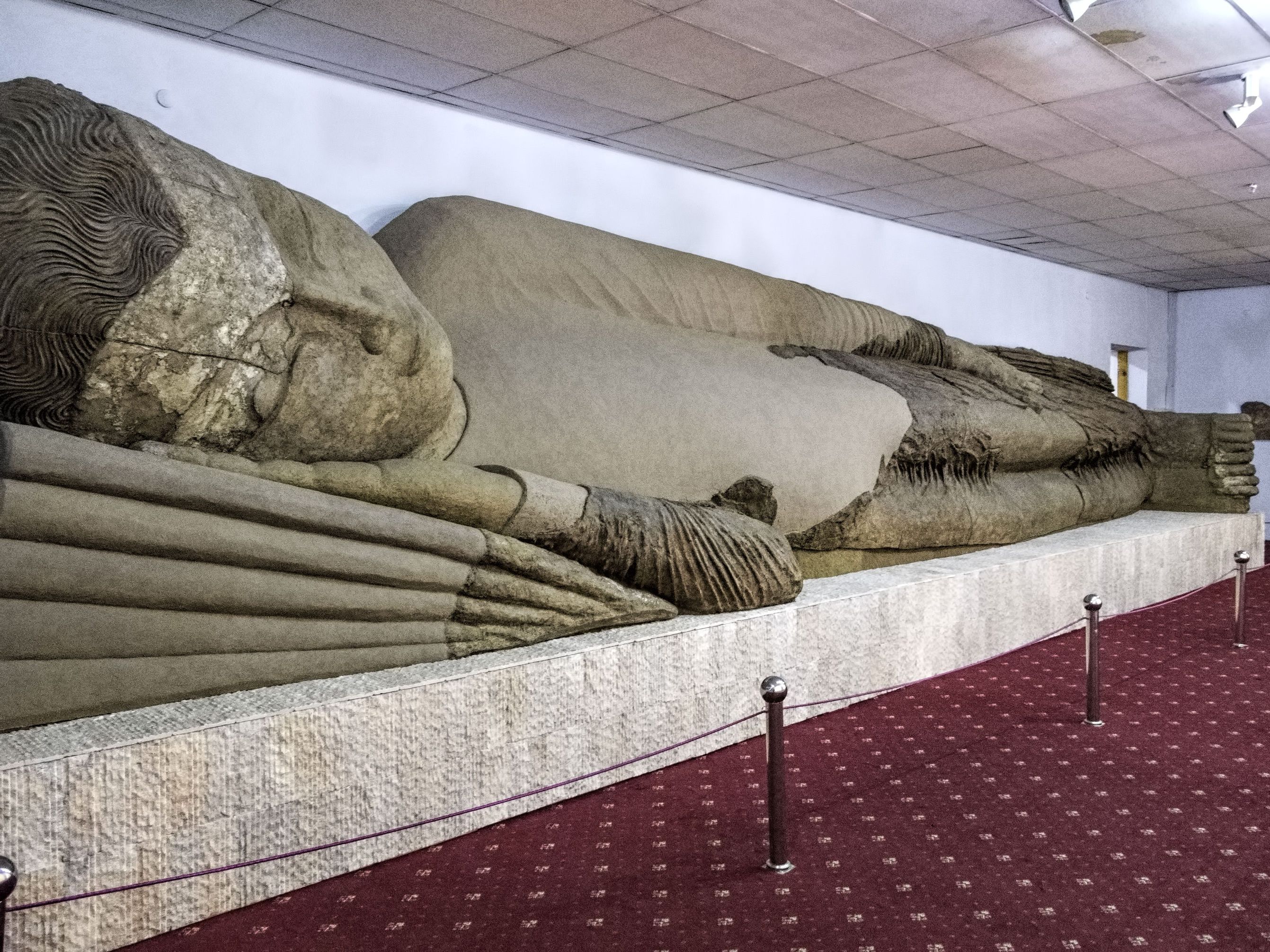

The most impressive and best known of the Ajina-Tepa findings was the giant horizontal statue of Buddha, also Known as Buddha in Nirvana, which was located in the eastern corridor of the monastery. It was discovered in 1966. Parts of the statue’s clothing was polychrome when it was discovered. The statue was made of clay. It was around 1,500 years old and almost 13 metres long. This statue is considered to be largest clay Buddha in Nirvana anywhere in the world and one of brightest Buddhist relics in world culture.
A long and difficult path was passed before the restoration of the statue was completed. In September 2000, the statue was placed in one of the halls of the Tajik National Museum of Antiquities. This statue is considered the largest in Central Asia after the destruction of the statue of Buddha in Bamiyan (Afghanistan) at the beginning of 2000 by the Taliban.
Gallery








Travelling to the Site
The site can be easily reached by car travelling from the city of Bokhtar. The city itself can be reached by buses, minibus, private taxi from the capital city of Dushanbe. Bokhtar is located 100 kilometres (62 mi) south of Dushanbe. Bokhtar is the largest city in the southern Tajikistan.